PCOS and pregnancy
7-minute read
What is PCOS?
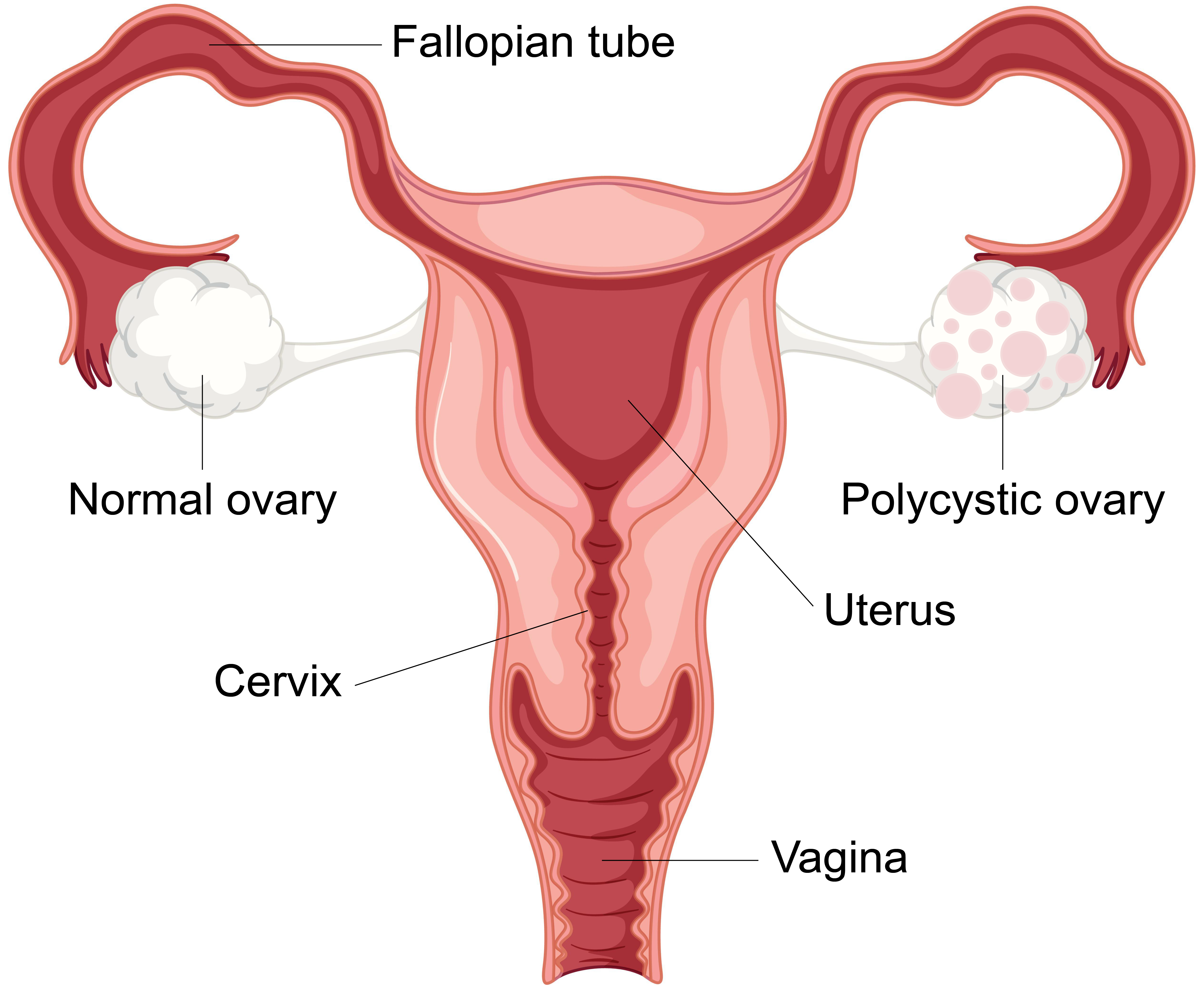
Polycystic ovarian syndrome, or PCOS, is a common condition.
People with PCOS can have:
- higher than normal levels of androgens (male-type hormones)
- problems with ovulation (the release of eggs from the ovaries)
- multiple cysts on the ovaries
This can affect your menstrual cycle, fertility and appearance.
If you have PCOS you may struggle to become pregnant and may be at higher risk of developing some pregnancy complications.
What are the symptoms of PCOS?
There are many signs and symptoms that are associated with PCOS. These can include:
- irregular menstrual periods
- cysts on the ovaries
- infertility
- weight gain
- acne
- depression
- excessive face and body hair
- thinning or balding head hair
- insulin resistance (where your cells don't respond to insulin and your blood sugar levels rise)
Some of these symptoms (such as acne, excess face and body hair, and scalp hair loss) are due to increased levels of the hormones called androgens. These hormones are found in all females, but those with PCOS have slightly higher amounts.
CHECK YOUR SYMPTOMS — If you are feeling unwell and not sure what to do next, check your symptoms using the healthdirect Symptom Checker tool.
How is PCOS diagnosed?
It often takes a while to get a PCOS diagnosis. This is because the condition can mimic other problems. Sometimes, people only find out that they have PCOS when they have tests to find out why they are having trouble getting pregnant.
If you think you might have PCOS, see your doctor. Early diagnosis means that your symptoms can be treated early.
At your appointment, your doctor will:
- ask about your symptoms
- ask for your medical history
- examine you
Your doctor may also recommend blood tests and an ultrasound scan to look for any cysts in the ovaries.
In general, to be diagnosed with PCOS, you need to have 2 out of 3 of the following;
- irregular periods, or no periods
- symptoms due to increased levels of androgen hormones, or a blood test showing you have increased levels of androgen hormones
- an ultrasound scan showing multiple cysts on your ovary or ovaries
FIND A HEALTH SERVICE — The Service Finder can help you find doctors, pharmacies, hospitals and other health services.
Will PCOS affect my fertility?
If you have PCOS, you might struggle to get pregnant.
Fortunately, with lifestyle changes or infertility treatment, most people with PCOS can become pregnant. Talk to your doctor or fertility specialist for individual advice for your situation.
Can PCOS increase my risk of complications during pregnancy?
Having PCOS can increase your risk of some complications during pregnancy, such as:
- high blood pressure
- gestational diabetes
- premature birth
If you have PCOS, you are also at increased risk of having a baby larger than expected for their gestational age. This comes with a higher risk of needing a caesarean delivery.
Babies born to people with PCOS have a higher chance of being admitted to a newborn intensive care unit.
Pregnant women with PCOS may have a higher risk of miscarriage and stillbirth. However, more research is needed in this area.
If you have PCOS and are pregnant, it is important you talk with your doctor. The risk of these complications can be reduced by monitoring your PCOS symptoms and taking extra care during your pregnancy.
What steps can I take to look after my health?
You can make lifestyle changes to manage your PCOS and look after your health. These include:
- maintaining a healthy weight
- eating healthily
- exercising
- managing stress
- getting enough sleep
These lifestyle changes can reduce the symptoms of PCOS and improve your chance of falling pregnant.
If you are overweight, a 5% to 10% loss in weight can increase your fertility.
Speak to your doctor for guidance on how to make effective lifestyle changes.
How is PCOS treated?
Treatment for PCOS depends on each person. Speak to your doctor about the best treatment for you.
If you are trying to fall pregnant, your PCOS treatment will focus on:
- restoring regular ovulation
- weight loss
- improving your general health and wellbeing
If you have made lifestyle changes and are still struggling to fall pregnant, your doctor may order fertility tests. They may also prescribe fertility medicines to help you ovulate. In some cases, they may recommend surgery.
Another possibility is in vitro fertilisation (IVF), which offers the best chance of conception. However, this can be expensive and is usually only considered when all other options have been unsuccessful.
If you are not trying to fall pregnant, your PCOS treatment will focus on:
- reducing your symptoms
- reducing your risk of long-term health issues, including heart disease and type 2 diabetes
Speak to your doctor. They can help you manage your PCOS symptoms by providing:
- weight loss management strategies
- treatment for sleeping problems
- acne treatment
- medicines, including hormonal contraception (birth control) to manage irregular menstruation
Dealing with infertility and PCOS symptoms can be difficult. You may experience feelings of depression and anxiety. Your doctor can refer you to a counsellor or psychologist for your mental health.
Resources and support
Visit the Jean Hailes website for more information on PCOS and its complications.
Hormones Australia also supplies information on PCOS, including questions to ask your doctor.

Speak to a maternal child health nurse
Call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby to speak to a maternal child health nurse on 1800 882 436 or video call. Available 7am to midnight (AET), 7 days a week.
Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: July 2022


rendition-574c0b.png)